TL;DR
LMCache, the state-of-the-art KV cache layer library developed by LMCache Lab and the project’s open-source community, delivers breakthrough performance improvements to modern enterprise LLM inference frameworks, including the vLLM Production Stack and KServe. With fast and scalable caching of long-context KV cache, LMCache helps reduce inference costs and ensures SLOs for both latency and throughput at scale.
The New Bottleneck in AI Infrastructure
Large Language Model (LLM) inference has become foundational infrastructure across the AI ecosystem. Whether powering copilots, search engines, document understanding tools, or enterprise chatbots, most real-world AI applications route their workloads through GPU clusters running high-throughput inference engines.
But as usage grows, two performance bottlenecks dominate, particularly in long-context queries:
- Cost Explosion — As user queries scale, so do the GPU costs.
- Latency SLOs — Meeting strict service-level objectives (SLOs) for both Time to First Token (TTFT) and Inter-Token Latency (ITL) is becoming harder.
These challenges demand smarter memory and cache management strategies. This is where LMCache steps in.
Introducing LMCache: A Smarter Cache for LLMs
Developed by LMCache Lab, LMCache is a high-performance KV cache management layer purpose-built for LLM inference. It is deeply integrated into the vLLM inference engine and supported natively in the vLLM upstream repo.
Why KV Caches Matter
In long-context scenarios—like ongoing conversations, repeated document analysis, or retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)—the same contextual history is used repeatedly. Yet traditional caching layers only store raw text, which forces the LLM to re-read and re-prefill context from scratch. KV cache is the internal representation (key-value pairs) LLMs use after prefill. Reusing KV cache directly is vastly faster and cheaper than reprocessing the text.
LMCache Capabilities
LMCache pushes the caching boundary in three dimensions:
Massive Scale
- Stores large volumes of KV cache, far beyond the limits of GPU memory
Blazing Speed
- Loads KV cache into GPU memory with CUDA-accelerated operators and pipelined data movement
Pluggable Storage
- Seamlessly integrates with diverse backends like MooncakeStore, Infinistore, Redis, DFS, and more
- Expands the effective memory of vLLM’s paged memory design
This transforms how inference engines manage historical context—turning it from a cost burden into a speed advantage.
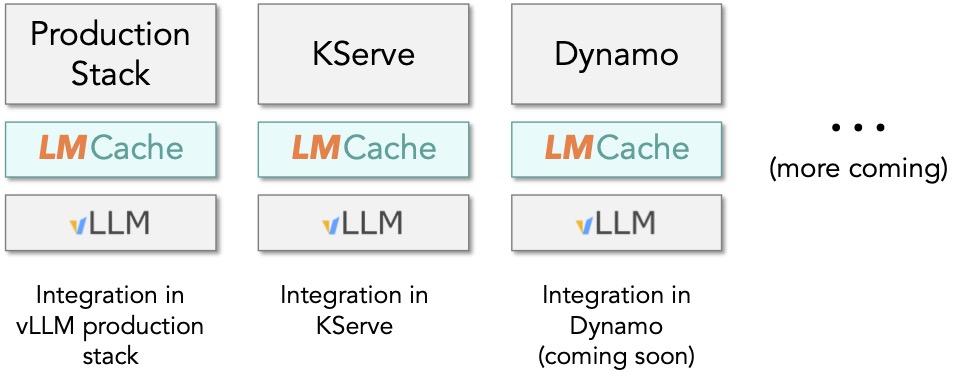
Integration in vLLM ecosystem projects
We are excited that LMCache has been integrated in multiple ecosystem projects, boosting the performance of vLLM’s deployments in the real world. Production stack, a part of the vLLM ecosystem, natively supports LMCache and routes requests based on where LMCache stores the KV cache. Recently, KServe also followed the suit PR.
LMCache architecture graph
We are also excited to partner with more ecosystem projects. Please contact us for collaborations!
Performance Benchmarking
LMCache is not just theory—it delivers tangible performance gains across real workloads. Feel free to reach out to us if versions of these inference frameworks are available. We will be happy to rerun and update the evaluation results.
📌 Real Usage (ShareGPT Trace)
On real-world traces from ShareGPT conversations, LMCache enables high KV reuse across multiple users and sessions, slashing both cost and latency.
Workload description: We randomly selected 200 users from the ShareGPT trace who have more than five rounds of conversation. The first two rounds are treated as context history, and from the third round onward, users send requests in a round‑robin sequence.
Workload generator script is here.
Model and hardware setup:
- Model: meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct
- Hardware: 2x A100 (80G)
vLLM & versions and launch scripts
- vLLM Production Stack v0 (0.7.3): script w/o LMCache, script w/ LMCache
- vLLM Production Stack v1 (0.8.4): script w/o LMCache, script w/ LMCache
- Dynamo: script w/o LMCache (We simulated the performance of Dynamo with LMCache by assuming LMCache has the same improvement as in vLLM v0 production stack, because Dynamo uses the same vLLM version).
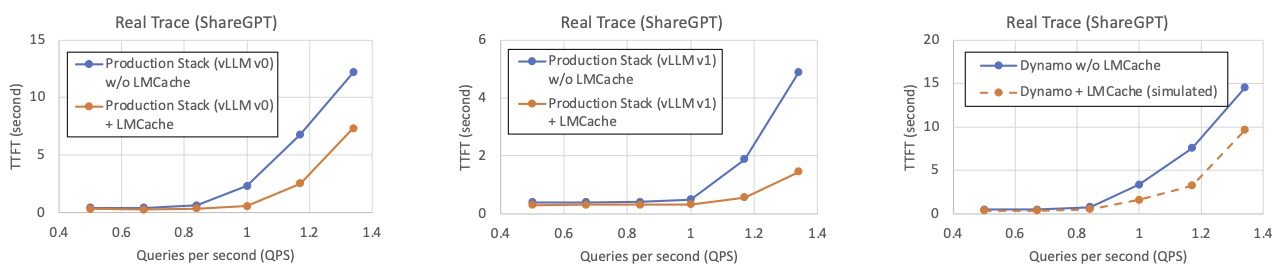
LMCache’s reduction in time to first token (TTFT)
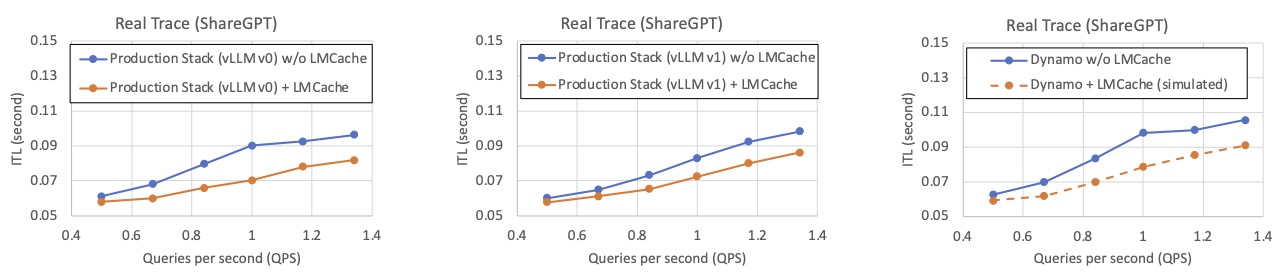
LMCache’s reduction in inter-token latency (ITL)
💬 Chat (Long Input → Short Output)
In chatbot-style workloads with long conversational histories and short generation outputs, LMCache minimizes redundant prefill time, yielding low TTFT even under high concurrency.
Workload description: Inspired by our production deployments, we create workloads that emulate a typical chat-bot document analysis workload. By default, each LLM query input has 20K tokens and a unique question, and the LLM output is an answer of 100 tokens. The context of each query is randomly selected from 15 documents, and to prevent the same document being queried too many times, each document is used as the context in only about 20 LLM inputs.
Workload generator script is here.
Model and hardware setup:
- Model: meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
- Hardware: 1x A100 (40G)
vLLM & versions and launch scripts vLLM Production Stack v0 (0.7.3): script w/o LMCache, script w/ LMCache vLLM Production Stack v1 (0.8.4): script w/o LMCache, script w/ LMCache Dynamo: script w/o LMCache (We simulated the performance of Dynamo with LMCache by assuming LMCache has the same improvement as in vLLM v0 production stack, because Dynamo uses the same vLLM version).
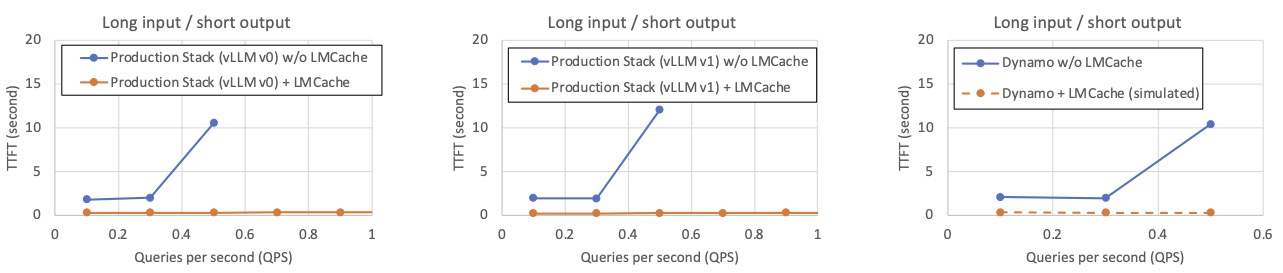
LMCache’s reduction in time to first token (TTFT)
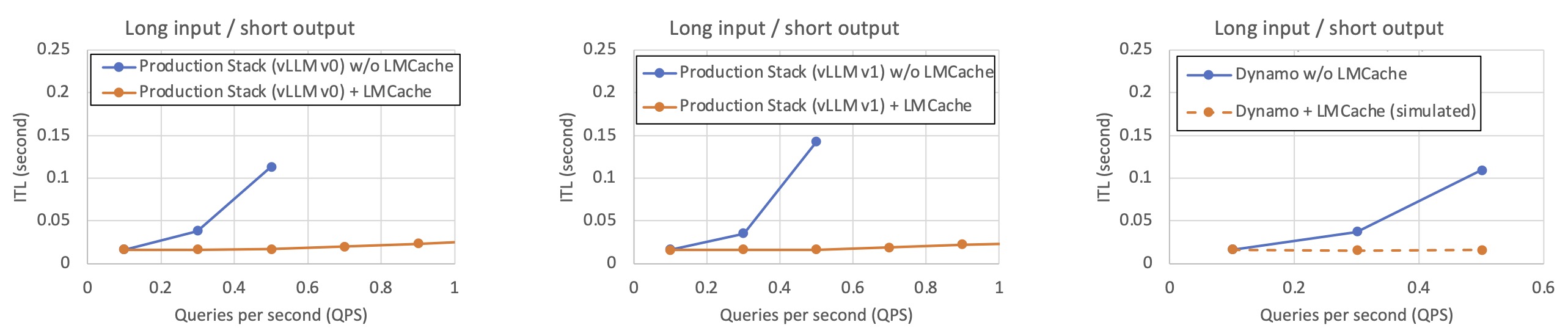
LMCache’s reduction in inter-token latency (ITL)
📄 Document Analysis (Short Input → Short Output)
For tasks like document Q&A or classification, where input contexts are short but frequently repeated, LMCache avoids reprocessing and boosts throughput significantly.
Workload description: Inspired by our production deployments, we create workloads that emulate a typical chat-bot document analysis workload. By default, each LLM query input has around 400 tokens and a unique question, and the LLM output is an answer of 20 tokens. The context of each query is randomly selected from 320 documents, and to prevent the same document being queried too many times, each document is used as the context in only about 20 LLM inputs.
Workload generator script is here.
Model and hardware setup:
- Model: meta-llama/Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct
- Hardware: 2x A100 (80G)
vLLM & versions and launch scripts are same as ShareGPT experiment
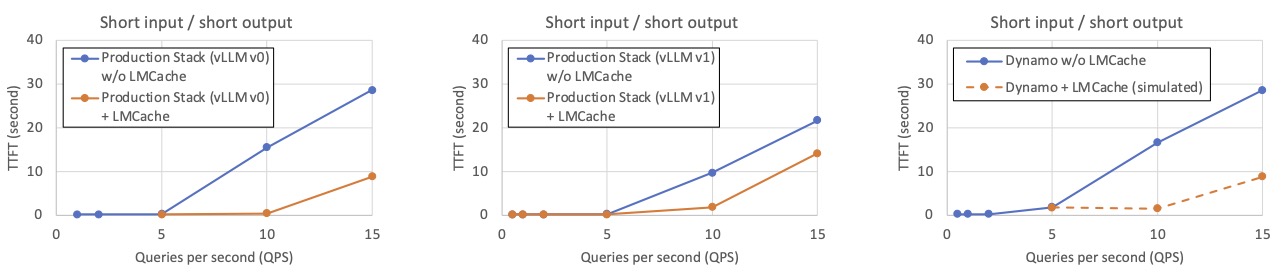
LMCache’s reduction in time to first token (TTFT)
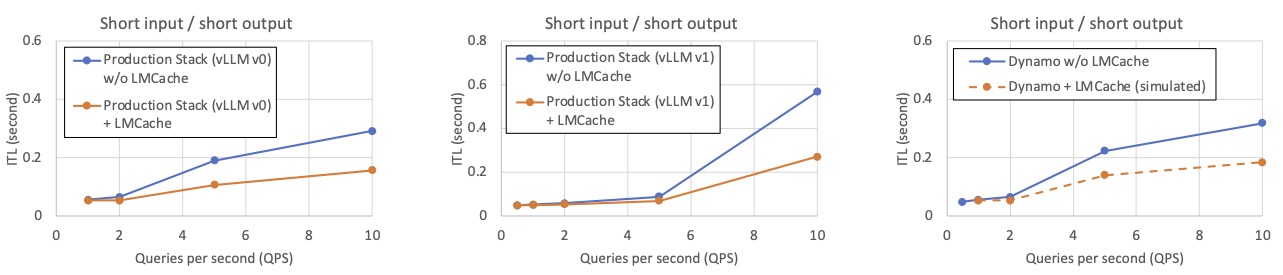
LMCache’s reduction in inter-token latency (ITL)
More Performance Wins
LMCache is also a leader in next-gen LLM system design, thanks to:
📚 High-Speed RAG Support
As shown in this blog, LMCache accelerates RAG pipelines by caching post-retrieval context embeddings in KV form, enabling:
- Up to 4.5× higher throughput on RAG workloads
- Faster recall from remote memory layers
- Low-latency generation even with dynamic retrieval
🚀 State-of-the-Art Prefill-Decoding Disaggregation
As detailed here, LMCache supports disaggregated prefill (DP), separating the KV generation and decoding stages of inference. This minimizes cross-interference and supports consistent decoding latency even under high load, achieving:
- Up to 5× lower inter-token latency
- Compatibility with Nvidia’s NIXL library and DP-aware schedulers in vLLM
Join the LMCache Ecosystem
LMCache is rapidly expanding its integration footprint. In addition to vLLM production stack and KServe, it’s in the process of being integrated in NVIDIA’s Dynamo, a modular framework for distributed LLM inference. Together, they demonstrate the power of composable open-source stacks for enterprise AI deployment.
We’re actively seeking partnerships with LLM inference frameworks and cloud providers interested in:
- KV cache optimization
- Disaggregated inference pipelines
- High-efficiency on-prem or VPC-based deployments
Let’s make AI infrastructure faster, cheaper, and smarter—together.
Try LMCache: https://github.com/LMCache/LMCache Follow us on Linkedin, Twitter